Python -- 內建函數
頭前 轉厝 後壁| abs() | dict() | help() | min() | setattr() |
| all() | dir() | hex() | next() | slice() |
| any() | divmod() | id() | object() | sorted() |
| ascii() | enumerate() | input() | oct() | staticmethod() |
| bin() | eval() | int() | open() | str() |
| bool() | exec() | isinstance() | ord() | sum() |
| bytearray() | filter() | issubclass() | pow() | super() |
| bytes() | float() | iter() | print() | tuple() |
| callable() | format() | len() | property() | type() |
| chr() | frozenset() | list() | range() | vars() |
| classmethod() | getattr() | locals() | repr() | zip() |
| compile() | globals() | map() | reversed() | __import__() |
| complex() | hasattr() | max() | round() | |
| delattr() | hash() | memoryview() | set() |
- copyright
- license
- credits
- help()
- dir()
- quit()
- exit()
- import this
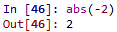
abs(): 計算絕對值
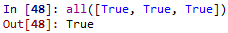
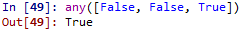
all() & any():
bin()、oct() & hex(): bin()傳回二進位碼,oct()傳回八進位碼,而hex()傳回十六進位碼

bool()、int()、float()、str(): 宣告或轉換變數

complex():傳回複數

list()、 tuple()、 dict()、 set() & frozenset()
dir() & help()
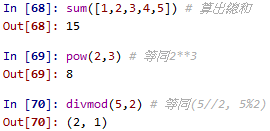
sum()、pow() & divmod(): 這三個方法幫我們計算總合,次方與相除之商餘
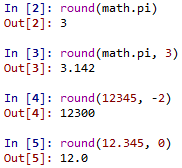
round(n): round(n)可以幫我們進位,如果n>0,是進位到小數後幾n位,n<0則是進位到整數第n位,若沒輸入(或是0)則為整數位

min() & max()

sorted() & reverse()





format()、len()、print()、type()、input() & range()
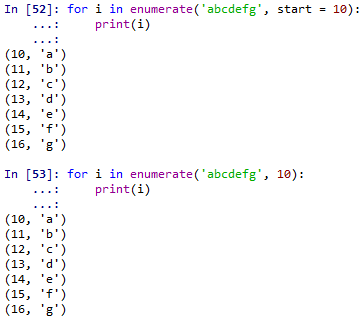
enumerate(): enumerate()幫我們將一個iterable的物件編號,並傳回tuple


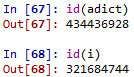
id(x): Python內的每一個物件都有固定的編號(id)
eval(): eval()這個函數需要輸入一個算式指令的字串,而他可以幫我們預測評估傳回值

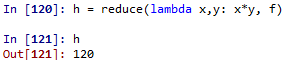
filter()、map() & reduce(): 此三方法皆需要將函數應用在一個iterable物件上,但是目的不同



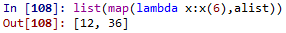

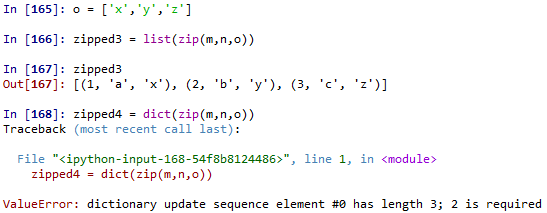
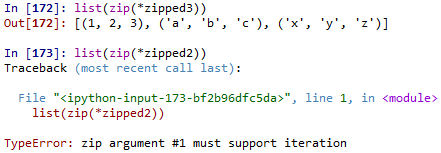
zip(): zip(*iterable)接受一系列的iterable物件,然後將對應位置的元素打包成一個tuple